So you’ve heard the term “Software as a Service” floating around, but you’re not quite sure what it means? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. In simple terms, Software as a Service, or SaaS for short, refers to a cloud computing model where software applications are provided over the internet on a subscription basis. Instead of purchasing and installing software on your own computer, you can access it through a web browser, making it more convenient and cost-effective. Sounds intriguing, right? Well, let’s dig a little deeper into the world of SaaS and explore its benefits and implications.
Overview
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model that allows you to access software applications over the internet. Instead of installing and maintaining the software on your own devices, you can simply use it through your web browser. SaaS provides a flexible and cost-effective solution for businesses and individuals who need access to various software applications.
Definition
SaaS refers to a software delivery model where applications are hosted on remote servers and accessed by users over the internet. It eliminates the need for users to install and maintain software on their own devices. Instead, they can access the software and its features through a web browser. The software is centrally managed by the SaaS provider, relieving users of the tedious tasks of software installation, updates, and maintenance.
Advantages
One of the primary advantages of SaaS is its ease of use. With SaaS, you can access and use software applications instantly without having to go through the complex installation process. All you need is a compatible web browser and an internet connection. This makes SaaS particularly popular among individuals and businesses with limited technical expertise.
Cost-effectiveness is another major advantage of SaaS. Instead of purchasing software licenses upfront, SaaS allows you to pay on a subscription basis. This subscription-based pricing model ensures that you only pay for what you need and use. Additionally, SaaS eliminates the need for costly hardware infrastructure and regular software updates, reducing overall expenses.
Disadvantages
While SaaS offers numerous advantages, it is not without its disadvantages. One major concern is the dependence on the internet. Since SaaS applications are accessed over the internet, any disruption in internet connectivity can hinder access to the software. This can be problematic, especially in areas with unreliable or limited internet access, and for users who require continuous access to critical software.
Another potential disadvantage of SaaS is the lack of customization options. Since the software applications are hosted and managed by the SaaS provider, users may have limited control over customizing the software to meet their specific needs. This can be a drawback for businesses that require highly tailored software solutions.
Key Concept
To understand SaaS fully, it is essential to grasp the key concepts that underpin its functionality. These concepts include the delivery model, subscription-based pricing, and cloud computing.
Delivery Model
The delivery model of SaaS involves the hosting of software applications on remote servers, which are then accessed by users over the internet. This eliminates the need for software installation on individual devices and allows for easy access and use through web browsers. The software is delivered to users as a service, enabling them to utilize its features without dealing with technical complexities.
Subscription-Based Pricing
SaaS employs a subscription-based pricing model where users pay on a periodic basis (monthly, quarterly, or annually) to access and use the software. This pricing structure is flexible and adaptable to different user needs. It ensures that users only pay for the software and features they require, making it a cost-effective solution for both individuals and businesses.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing forms the foundation of SaaS. It involves the storage and processing of data and applications on remote servers, which are accessed over the internet. Cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure for SaaS to function effectively. It offers scalability, reliability, and accessibility, enabling SaaS providers to deliver software applications to users seamlessly.
This image is property of images.spiceworks.com.
Differentiation
SaaS differs from other software delivery models and deployment options. Understanding the distinctions between SaaS and PaaS (Platform as a Service), IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), and on-premises software is crucial.
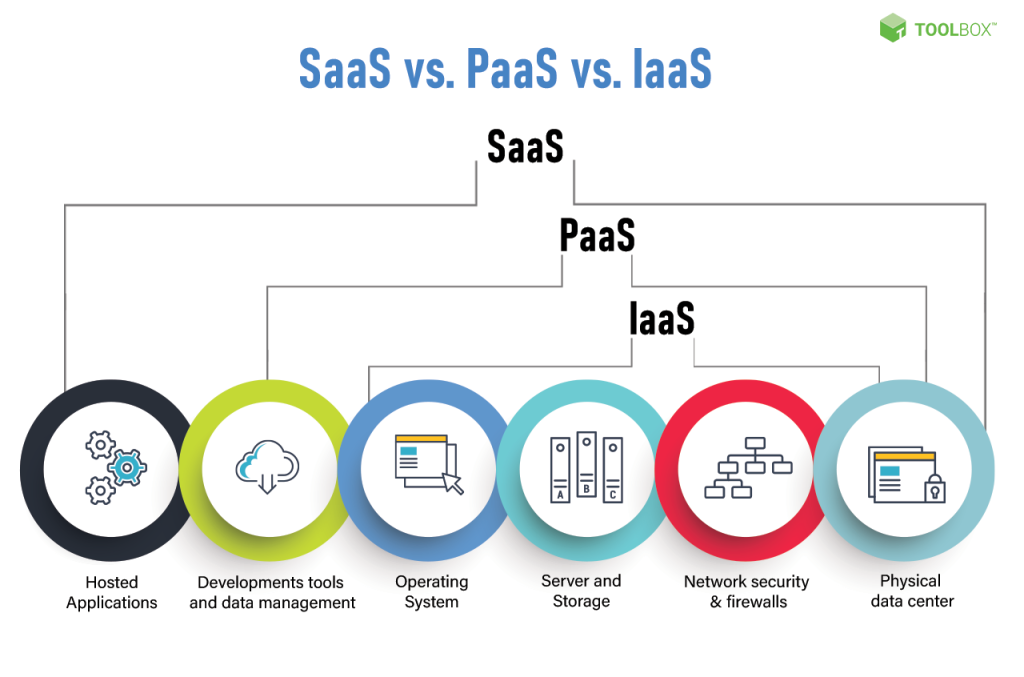
SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS are the three primary categories of cloud computing services. While they share similar cloud-based characteristics, each has its own focus and functionality.
SaaS focuses on providing complete software applications over the internet, allowing users to access and use these applications without the need for installation or maintenance. PaaS, on the other hand, offers a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. It provides tools and infrastructure for application development and management. IaaS focuses on providing virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines and storage, allowing users to build and manage their own infrastructure in the cloud.
SaaS vs. On-Premises Software
The key distinction between SaaS and on-premises software lies in the deployment method. SaaS applications are hosted and managed by the SaaS provider on remote servers, while on-premises software is installed and operated directly on the user’s local hardware infrastructure. SaaS offers the advantage of easy access, cost-effectiveness, and reduced maintenance, whereas on-premises software provides users with greater control over customization and data security.
Features
SaaS offers several essential features that make it an attractive choice for individuals and businesses. These features include accessibility, scalability, automatic updates, and collaboration.
Accessibility
One of the notable features of SaaS is its accessibility. Since SaaS applications are accessed through web browsers, users can use them from anywhere and on different devices. Whether you are at home, in the office, or traveling, as long as you have an internet connection and a compatible device, you can access your software applications seamlessly. This makes SaaS ideal for remote work, collaboration with team members, and increased productivity.
Scalability
SaaS offers scalability, allowing you to scale your usage up or down based on your needs. Whether you need to add additional user licenses, storage space, or features, SaaS providers can accommodate your requirements quickly. This scalability eliminates the need for upfront hardware investments and allows businesses to flexibly adjust their software usage as their needs change.
Automatic Updates
SaaS relieves users of the burden of software updates. The responsibility for software maintenance, including updates and patches, lies with the SaaS provider. Users do not have to worry about installing updates or dealing with compatibility issues. Automatic updates ensure that users always have access to the latest features and security enhancements without any effort from their end.
Collaboration
Collaboration is made easier with SaaS applications. Multiple users can simultaneously access and collaborate on documents and projects through the shared platform. Real-time editing, commenting, and version control features enable seamless teamwork and enhance productivity. With SaaS, teams can work together remotely, eliminating the need for physical proximity and enabling efficient collaboration across different locations.
This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
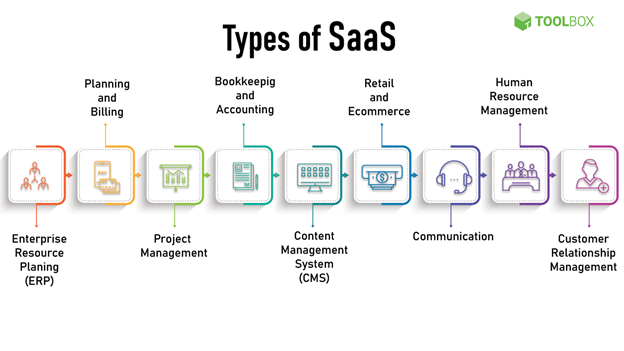
Examples
Several well-known software applications and providers fall under the SaaS category. Here are a few examples to illustrate the variety of SaaS offerings:
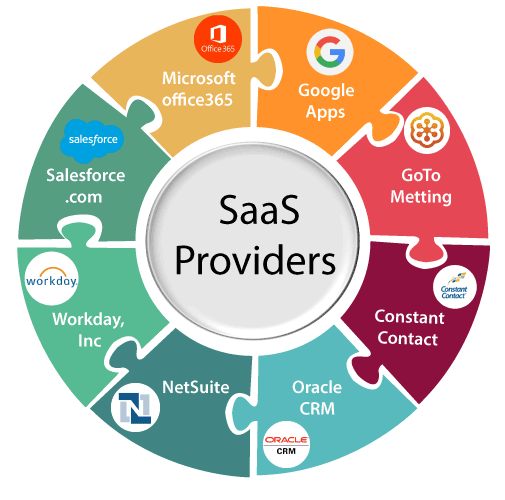
Salesforce
Salesforce is a renowned customer relationship management (CRM) platform that operates on the SaaS model. It provides businesses with a comprehensive suite of tools for managing customer interactions, sales processes, marketing campaigns, and customer service. Salesforce offers scalable and customizable solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses across various industries.
Microsoft Office 365
Microsoft Office 365 is a cloud-based productivity suite that includes familiar applications such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook. It enables individuals and businesses to access, create, edit, and share documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and emails online. Office 365 provides a seamless collaboration environment, allowing users to work on files simultaneously and store them securely in the cloud.
Google Workspace
Formerly known as G Suite, Google Workspace is a collection of cloud-based productivity tools offered by Google. It includes applications like Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, Google Sheets, and Google Slides. Google Workspace enables efficient communication, collaboration, and document management for individuals, teams, and organizations of all sizes. Users can create, store, and share files, collaborate in real-time, and access their work from any device with internet connectivity.
Potential Risks
While SaaS offers various advantages, it is essential to consider potential risks when opting for this software delivery model.
Vendor Lock-In
One significant risk of SaaS is the potential for vendor lock-in. Switching from one SaaS provider to another may not be straightforward, as data and processes can become tightly integrated with a specific SaaS platform. The migration of data and workflows to a different provider can be complex, time-consuming, and costly. It is crucial to carefully evaluate vendor contracts and consider potential exit strategies to mitigate the risks associated with vendor lock-in.
Data Security
Data security is a critical concern in any software environment, and SaaS is no exception. Since SaaS applications require sensitive data to be stored and processed in the cloud, it is crucial to ensure that appropriate security measures are in place. SaaS providers should implement robust security protocols, encryption technologies, and regular security audits to protect their users’ data. Users must also take measures to secure their own accounts and use strong passwords to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
This image is property of images.spiceworks.com.
Future Trends
The future of SaaS holds exciting possibilities, with emerging trends that will shape the industry further.
Integration with AI
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology continues to evolve, integration with SaaS applications is becoming more prevalent. AI algorithms and machine learning capabilities are being incorporated into SaaS offerings to enhance productivity, improve data analysis, automate routine tasks, and provide personalized user experiences. AI integration will undoubtedly drive further innovation and efficiency in SaaS applications, benefiting both individuals and businesses.
Emergence of SaaS Marketplaces
SaaS marketplaces are emerging as platforms that connect SaaS providers and customers in a centralized ecosystem. These marketplaces offer a wide range of SaaS applications, allowing users to discover, compare, and acquire software solutions that best suit their needs. SaaS marketplaces streamline the process of finding, evaluating, and implementing SaaS applications, making it easier for users to navigate the SaaS landscape and access the software they require.
In conclusion, SaaS offers a compelling software delivery model with numerous advantages, including ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility. While it may have some disadvantages, such as dependence on internet connectivity and limited customization options, the benefits of SaaS make it an attractive option for individuals and businesses alike. With its scalability, automatic updates, collaboration features, and examples like Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace, SaaS has proven its value in empowering users to work efficiently and collaboratively. As the SaaS market continues to evolve, trends such as integration with AI and the emergence of SaaS marketplaces will shape its future, promising even more innovation and convenience for users. However, it is crucial to consider potential risks such as vendor lock-in and data security when adopting SaaS, ensuring appropriate measures are taken to mitigate these risks and protect both users and their data.