So you want to enter the world of software development, but you’re not quite sure where to start? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. In this article, we’ll be exploring the burning question on every aspiring developer’s mind: which software skill is most in demand? With the rapid advancements in technology and the ever-increasing demand for software solutions, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of the most sought-after skills in the industry. Whether you’re a seasoned developer looking to enhance your skillset or a beginner setting foot in the software world, this article will provide you with valuable insights to help you make informed decisions about your career path. So let’s dive right in and discover the software skill that will set you apart from the competition.
This image is property of www.i-programmer.info.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly evolving field that focuses on developing computer systems that can perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence. AI encompasses various subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and robotics. These subfields contribute to the advancement of AI technology by enabling machines to learn, understand and interpret data, and interact with their surroundings.
1.1 Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables machines to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. It involves the development of algorithms that can automatically learn patterns and make predictions or decisions based on data. Machine learning models are trained on large sets of data, allowing them to generalize and make accurate predictions on new, unseen data. This technology has widespread applications across industries, such as predicting customer behavior, optimizing manufacturing processes, and enabling self-driving cars.
1.2 Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) focuses on enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. NLP algorithms analyze and process text or speech data to extract meaning, sentiment, or intent. This field has given rise to technologies like virtual assistants, chatbots, and language translation tools. NLP plays a crucial role in enhancing communication between humans and machines, making interactions more intuitive and seamless.
1.3 Computer Vision
Computer vision involves developing algorithms and systems that allow machines to understand and interpret visual information. This technology aims to enable computers to perceive, analyze, and make sense of images or videos, similar to how humans do. Computer vision has practical applications in various domains, including autonomous vehicles, facial recognition systems, and medical imaging. It plays a pivotal role in enabling machines to “see” and understand the world around them.
1.4 Robotics
Robotics combines AI, machine learning, and other technologies to design and develop intelligent machines that can perform physical tasks autonomously. Robotic systems are equipped with sensors, actuators, and programming that enable them to perceive their environment, make decisions, and perform precise movements. Robotics has applications in fields such as manufacturing, healthcare, and exploration. As the field advances, robots are becoming more capable of interacting with humans and adapting to dynamic environments.
2. Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has become a critical concern in today’s digital landscape. As technology continues to advance, so do the threats and vulnerabilities associated with it. This has led to an increasing demand for individuals with expertise in cybersecurity to protect sensitive data and systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
2.1 Network Security
Network security focuses on protecting computer networks from unauthorized access, misuse, or disruption. Professionals in network security are responsible for designing and implementing security measures to safeguard network infrastructure, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs). They ensure that network communication remains secure and uninterrupted, mitigating the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
2.2 Ethical Hacking
Ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing or white-hat hacking, involves simulating cyber attacks on computer systems to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Ethical hackers use their skills and knowledge to expose potential risks and help organizations strengthen their security measures. This field requires a deep understanding of various hacking techniques, network protocols, and software vulnerabilities. Ethical hackers play a crucial role in preventing malicious attacks and securing systems against cyber threats.
2.3 Incident Response
Incident response refers to the processes and procedures followed in the event of a cybersecurity incident or breach. Professionals in incident response are responsible for detecting, analyzing, and responding to security incidents in a timely and effective manner. This involves identifying the source of the incident, containing and mitigating its impact, and conducting forensic investigations to prevent future occurrences. Incident response teams are crucial in minimizing damages and restoring normalcy after a cyber attack.
2.4 Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice of securing communication and data by encrypting information to make it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Cryptography relies on mathematical algorithms and techniques to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. Cryptographers design and implement cryptographic systems, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure during storage and transmission. Cryptography is fundamental to various cybersecurity applications, such as secure communication protocols, digital signatures, and secure storage systems.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals store, manage, and process data. It involves the delivery of computing services over the internet, providing on-demand access to resources and eliminating the need for physical infrastructure. As organizations increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, the demand for skilled professionals in cloud computing has surged.
3.1 Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services, including storage, computing power, database management, and content delivery. Professionals skilled in AWS have expertise in deploying, securing, and managing applications and services on the AWS platform. This includes knowledge of services such as EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), S3 (Simple Storage Service), and RDS (Relational Database Service). AWS certification is highly valued in the industry, as it demonstrates proficiency in using the AWS platform effectively and securely.
3.2 Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is another prominent cloud computing platform that provides a comprehensive suite of services for building, deploying, and managing applications and services. Azure offers a wide range of services, including virtual machines, databases, AI services, and IoT solutions. Professionals skilled in Microsoft Azure possess the knowledge and expertise to design and implement scalable and secure cloud-based solutions. Azure certification validates proficiency in Azure services and demonstrates the ability to leverage Microsoft’s cloud platform effectively.
3.3 Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is Google’s cloud computing offering, providing a range of cloud-based services and tools for developing and deploying applications. GCP offers services such as virtual machines, cloud storage, machine learning, and BigQuery for data analytics. Proficiency in GCP entails understanding its various services, designing scalable architectures, and optimizing resource utilization. Google Cloud certification demonstrates expertise in leveraging GCP’s capabilities to build and deploy robust cloud solutions.
4. Data Science
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that combines statistics, programming, and domain knowledge to extract insights and value from large volumes of data. As organizations generate massive amounts of data, the need for skilled data scientists has grown significantly. Data science encompasses various subfields, including data analytics, data visualization, data mining, and statistical analysis.
4.1 Data Analytics
Data analytics involves extracting actionable insights and patterns from complex data sets using various techniques, such as statistical analysis, data mining, and machine learning. Data analysts leverage tools and programming languages like Python or R to clean, transform, and analyze data, providing valuable insights to inform decision-making. Data analytics is used across industries for tasks such as market research, customer segmentation, and performance optimization.
4.2 Data Visualization
Data visualization focuses on presenting data in a visual and intuitive way to facilitate understanding and communicate insights effectively. Data visualization professionals employ tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Python libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn to create interactive visualizations and dashboards. Data visualization plays a crucial role in aiding data analysis and enabling stakeholders to comprehend complex data sets easily.
4.3 Data Mining
Data mining involves discovering patterns, relationships, and anomalies in large datasets. It uses techniques such as clustering, classification, and association rules to uncover hidden knowledge from data. Data mining techniques have applications in fraud detection, market basket analysis, and recommendation systems. Data mining professionals are skilled in programming languages such as Python or R and possess a deep understanding of algorithms and machine learning techniques.
4.4 Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis involves applying statistical models and techniques to analyze data and draw conclusions or make predictions. Statistical analysts use tools like Python, R, or statistical software packages (e.g., SPSS) to analyze data and interpret results. Statistical analysis plays a vital role in hypothesis testing, predictive modeling, and experimental design. Professionals in statistical analysis have a strong foundation in statistical theory and applied statistics, enabling them to make data-driven decisions.
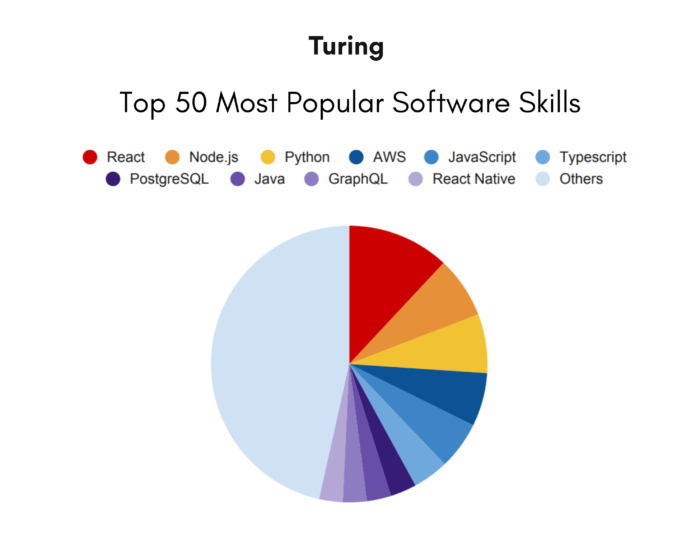
This image is property of www.turing.com.
5. Full Stack Development
Full stack development refers to the ability to develop both the front-end and back-end components of a web application. Full stack developers are proficient in multiple programming languages and frameworks, enabling them to work on both the client-side and server-side aspects of web development. They possess a broad skillset that includes front-end development, back-end development, database management, and web server administration.
5.1 Front-end Development
Front-end development involves designing and implementing the user interface of a web application. Front-end developers work with technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create the visual and interactive elements that users interact with. They are responsible for ensuring a seamless user experience by optimizing performance, responsiveness, and accessibility of web applications. Front-end development requires a strong understanding of web standards, user experience design, and responsive design principles.
5.2 Back-end Development
Back-end development focuses on designing and implementing the server-side logic and database connections of a web application. Back-end developers work with programming languages like Python, Java, or PHP, and frameworks like Django, Spring, or Laravel to build robust and scalable web applications. They handle tasks such as data processing, business logic implementation, and API development. Back-end development requires knowledge of server management, database systems, and security practices.
5.3 Database Management
Database management involves designing, implementing, and maintaining databases to store, organize, and retrieve data efficiently. Database administrators (DBAs) ensure data integrity, performance, and security by optimizing database structures, designing appropriate schemas, and implementing backup and recovery strategies. Proficiency in managing SQL-based databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle is essential for effective database management.
5.4 Web Server Administration
Web server administration focuses on configuring, deploying, and managing web server software to host websites and web applications. Web server administrators are responsible for maintaining server security, performance optimization, and troubleshooting server-related issues. They work with technologies like Apache, Nginx, or Microsoft IIS to ensure reliable and efficient web server operation. Web server administration skills are essential for deploying and managing web applications in production environments.
6. Mobile App Development
Mobile app development refers to the process of designing and building applications specifically for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. With the increasing ubiquity of mobile devices, the demand for skilled mobile app developers has surged. Mobile app development encompasses various platforms and technologies, including Android development, iOS development, and cross-platform development.
6.1 Android Development
Android development involves creating applications for the Android operating system, which powers a majority of the world’s smartphones. Android developers use programming languages like Java or Kotlin and development frameworks like Android Studio to build native Android applications. They work with APIs and libraries provided by the Android platform to develop feature-rich and user-friendly applications. Android development skills are essential for creating applications for the vast Android user base.
6.2 iOS Development
iOS development focuses on creating applications for Apple’s iOS operating system, which powers iPhones, iPads, and iPods. iOS developers use programming languages like Swift or Objective-C and development tools like Xcode to build native iOS applications. They leverage the iOS SDK (Software Development Kit) to access device-specific features and deliver a seamless and optimized user experience. iOS development skills are valuable in creating applications for Apple’s loyal and affluent user base.
6.3 Cross-platform Development
Cross-platform development involves creating applications that can run on multiple platforms, such as Android and iOS, using a single codebase. Cross-platform developers utilize frameworks and technologies like React Native, Xamarin, or Flutter to develop applications that share a common codebase but can be deployed on different platforms. Cross-platform development offers advantages in terms of code reusability, faster development cycles, and broader market reach.
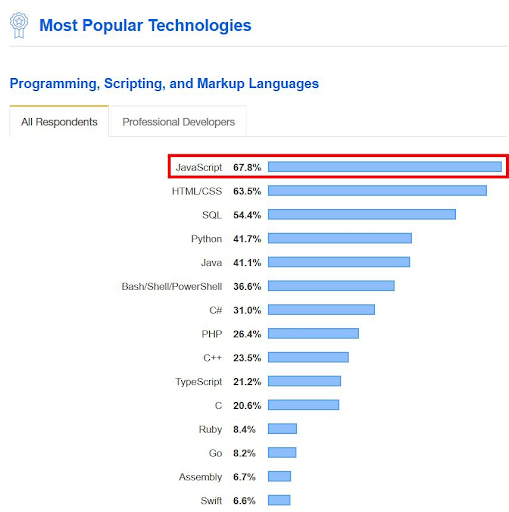
This image is property of www.digitalknights.co.
7. DevOps
DevOps is a set of practices and cultural philosophies that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to enable continuous delivery and deployment of applications. DevOps professionals bridge the gap between development and operations teams, enabling faster and more efficient software development cycles. DevOps encompasses practices such as continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), infrastructure as code (IaC), containerization, and monitoring and logging.
7.1 Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) refers to a set of practices and tools that automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software. CI pipelines ensure that code changes are continuously integrated, tested, and deployed to production environments, reducing the risk of errors and enabling faster feedback loops. CI/CD tools such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, or CircleCI are used to automate various stages of the software development lifecycle.
7.2 Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as code (IaC) involves managing and provisioning infrastructure resources using machine-readable definition files. IaC tools like Terraform, Ansible, or AWS CloudFormation enable developers and system administrators to define and configure their infrastructure using code rather than manual processes. This allows for reproducibility, version control, and scalability of infrastructure resources, leading to more efficient and consistent deployments.
7.3 Containerization
Containerization involves packaging applications and their dependencies into lightweight, isolated containers that can run consistently across different environments. Containerization technologies like Docker enable developers to create portable, self-contained units of software that can be deployed and scaled independently. Containers provide benefits such as easier deployment, scalability, and rapid application development, making them an essential part of modern DevOps workflows.
7.4 Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging involve collecting and analyzing data on the performance and behavior of applications and infrastructure. DevOps professionals use monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack to track key metrics, visualize system health, and identify issues or bottlenecks. Logging tools such as Splunk or Logstash capture logs generated by applications and systems, facilitating troubleshooting, performance analysis, and compliance auditing.
8. User Experience (UX) Design
User experience (UX) design focuses on creating products or services that are optimized for user satisfaction, usability, and interaction. UX designers employ various methodologies and techniques to understand user needs, design intuitive interfaces, and ensure a positive user experience. UX design encompasses subfields such as user research, wireframing and prototyping, usability testing, and information architecture.
8.1 User Research
User research involves understanding user behaviors, needs, and motivations through various research methods, such as surveys, interviews, and observations. UX designers conduct user research to gain insights into user preferences, pain points, and expectations, guiding the design process. User research helps in creating user-centric and effective designs that meet user expectations and deliver value.
8.2 Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping involve creating visual representations and interactive mockups of the user interface to demonstrate the design concept and functionality. UX designers use tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, or Figma to create wireframes and prototypes that capture the intended user experience. Wireframing and prototyping help in obtaining early feedback, iterating designs, and validating usability before implementation.
8.3 Usability Testing
Usability testing involves evaluating the usability and ease of use of a product or service by observing users interacting with it. UX designers conduct usability tests to identify usability issues, gather feedback, and make iterative improvements. Usability testing helps ensure that the design meets user expectations, addresses user pain points, and provides a satisfying and intuitive experience.
8.4 Information Architecture
Information architecture involves organizing and structuring information to facilitate efficient navigation and information retrieval. UX designers create information architectures by designing logical and intuitive content hierarchies, navigation systems, and search functionalities. Information architecture plays a crucial role in ensuring that users can find the information they need quickly and effortlessly, enhancing overall user experience.
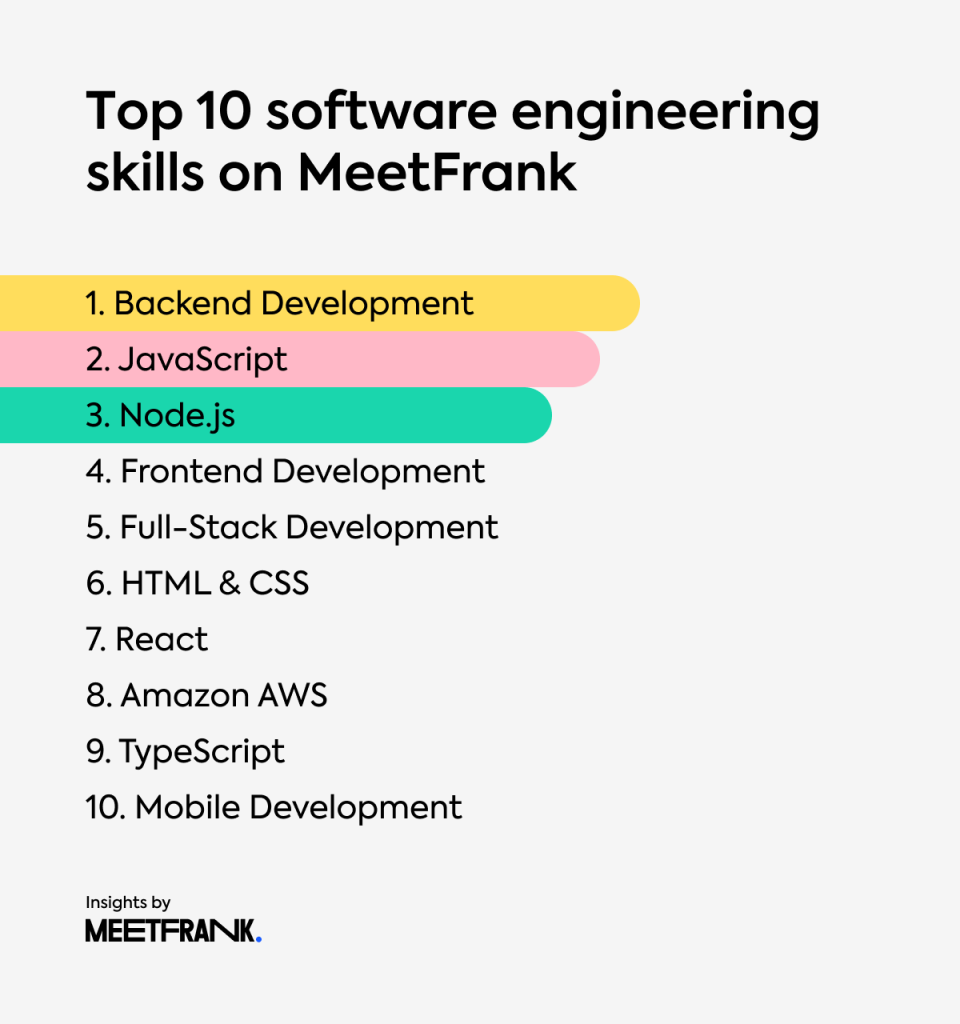
This image is property of meetfrank.com.
9. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has gained significant attention and recognition due to its potential to disrupt various industries through its decentralized and transparent nature. Blockchain allows for secure and tamper-proof transactions and data storage, removing the need for intermediaries and increasing trust and efficiency. Proficiency in blockchain technology encompasses subfields such as smart contracts, cryptocurrency development, distributed ledger technology (DLT), and decentralized applications (DApps).
9.1 Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries and enable secure and automated transactions on the blockchain. Professionals skilled in smart contract development use programming languages like Solidity (used in Ethereum) or Vyper to create smart contracts that automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts have applications in industries like finance, supply chain management, and decentralized finance (DeFi).
9.2 Cryptocurrency Development
Cryptocurrency development involves creating and managing digital currencies that leverage blockchain technology for secure and decentralized transactions. Cryptocurrency developers use blockchain platforms like Bitcoin or Ethereum to develop and maintain cryptocurrencies. They handle tasks like wallet management, transaction protocols, and security measures. Cryptocurrency development skills are vital in creating innovative digital currencies and exploring emerging opportunities in the blockchain space.
9.3 Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) refers to a decentralized database that securely records and stores information across multiple nodes or computers. DLT ensures transparency, traceability, and immutability of data, making it a powerful tool for industries like finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. Professionals skilled in DLT have deep knowledge of blockchain platforms and protocols like Hyperledger Fabric, Corda, or Quorum. They design and implement DLT solutions, considering factors like consensus mechanisms, data privacy, and interoperability.
9.4 Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Decentralized applications (DApps) are applications that run on a blockchain network, leveraging its decentralized and transparent nature. DApp developers use blockchain platforms like Ethereum, EOS, or Tron to build applications that leverage smart contracts and enable peer-to-peer interactions without relying on intermediaries. DApp development requires proficiency in blockchain technologies and frameworks, as well as frontend and backend development skills. DApps have the potential to disrupt sectors like finance, supply chain, and gaming by enabling direct and secure interactions between users.
10. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected physical devices that can communicate and exchange data using embedded sensors, actuators, and network connectivity. IoT technology enables the intelligent monitoring and control of devices and systems, leading to increased efficiency and automation in various domains. Proficiency in IoT encompasses subfields such as embedded systems, sensor networks, data analytics for IoT, and IoT security.
10.1 Embedded Systems
Embedded systems are computing systems designed to perform specific functions within larger systems or devices. They are integrated into various devices, such as smartwatches, home automation systems, or industrial machinery. Professionals skilled in embedded systems develop hardware and software solutions that enable efficient and reliable functioning of these devices. They have expertise in programming languages like C or C++, microcontrollers, and system integration.
10.2 Sensor Networks
Sensor networks involve the deployment of numerous interconnected sensors to collect and transmit data from the physical environment. Sensor network professionals design and manage networks of sensors that enable IoT systems to capture real-time data for monitoring, analysis, and control. They have knowledge of sensor technologies, data transmission protocols, and interoperability standards. Sensor networks have applications in environmental monitoring, smart cities, and industrial automation.
10.3 Data Analytics for IoT
Data analytics for IoT focuses on extracting valuable insights from the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices and sensors. IoT data analysts use statistical techniques, machine learning algorithms, and big data technologies to analyze, visualize, and derive meaningful information from IoT data. They identify patterns, anomalies, and trends that enable data-driven decision-making and optimization of IoT systems. Data analytics skills are essential in unlocking the full potential of IoT technologies.
10.4 IoT Security
IoT security refers to the practices and technologies implemented to safeguard IoT devices and networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. IoT security professionals design and implement security measures to protect IoT devices, networks, and data from potential vulnerabilities. They ensure secure device authentication, data encryption, and secure communication protocols. IoT security is crucial in preventing unauthorized access and ensuring the privacy and integrity of IoT systems.
In conclusion, the software skills mentioned above are currently in high demand in the industry. The advancements in AI, cybersecurity, cloud computing, data science, full stack development, mobile app development, DevOps, UX design, blockchain technology, and IoT continue to shape the technological landscape and create new opportunities. Whether you are interested in developing intelligent systems, securing digital infrastructure, analyzing data, building user-friendly applications, or exploring decentralized technologies, acquiring skills in these areas can open doors to exciting and rewarding careers. Stay curious, keep learning, and embrace the ever-evolving world of software technology.
This image is property of lh6.googleusercontent.com.